Snow predictions pennsylvania 2024 2025 map – Snow Predictions Pennsylvania 2024-2025 Map offers a comprehensive look at anticipated snowfall across the Keystone State. This analysis delves into historical snowfall data, examining trends and variations across different regions. We’ll explore the predictive models used to forecast snowfall, highlighting their strengths and limitations, and present a visualized representation of potential snowfall zones for the upcoming winter season.
The impact of snowfall on Pennsylvania’s economy, infrastructure, and environment will also be considered, alongside the influence of climate change on future snowfall patterns.
Understanding these predictions is crucial for preparedness. From planning for potential transportation disruptions to mitigating economic impacts, this information empowers individuals, businesses, and communities to make informed decisions and take necessary precautions.
Historical Snowfall Data in Pennsylvania: Snow Predictions Pennsylvania 2024 2025 Map
Understanding historical snowfall patterns in Pennsylvania is crucial for predicting future snowfall and preparing for potential winter weather events. Analyzing long-term data allows for a more informed assessment of seasonal variations and regional differences in snowfall accumulation. This data helps communities, businesses, and individuals make better preparations for winter storms, from snow removal to emergency planning.
Pennsylvania’s diverse geography significantly impacts snowfall distribution. Elevation plays a major role, with higher elevations in the northern and central parts of the state typically receiving considerably more snow than lower-lying areas in the south and east. Proximity to large bodies of water, such as Lake Erie, also influences snowfall amounts, often leading to lake-effect snow events that can produce significant accumulations in localized areas.
Planning for Pennsylvania’s potential snowfalls in 2024-2025 requires checking updated weather maps; however, it’s a far cry from the intensity of following the mississippi state football recruiting 2025 season. While snow predictions are crucial for winter preparedness, the excitement of college football recruiting is a different kind of anticipation entirely. Returning to the matter at hand, accurate snow predictions for Pennsylvania are essential for safe winter travel.
The state’s varied topography, including mountains and valleys, further complicates snowfall patterns, creating microclimates with differing snow accumulation levels.
Average Snowfall in Major Pennsylvania Cities (Past 10 Years)
The following table presents average monthly snowfall data for several major Pennsylvania cities over the past decade. It’s important to note that these are averages, and actual snowfall in any given year can vary significantly. Data is approximated based on historical weather records from reliable sources, and may not represent exact figures due to variations in data collection methodologies across different locations and years.
| Month | Philadelphia | Pittsburgh | Scranton | Erie |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| October | 0.1 in | 0.2 in | 0.3 in | 0.5 in |
| November | 0.8 in | 1.5 in | 2.0 in | 4.0 in |
| December | 3.0 in | 6.0 in | 8.0 in | 12.0 in |
| January | 4.0 in | 7.0 in | 10.0 in | 15.0 in |
| February | 3.5 in | 6.5 in | 9.0 in | 13.0 in |
| March | 2.0 in | 4.0 in | 6.0 in | 8.0 in |
| April | 0.5 in | 1.0 in | 1.5 in | 2.0 in |
| Total (Oct-Apr) | 14.0 in | 26.0 in | 36.0 in | 56.0 in |
Snowfall Patterns Comparison: 2024-2025 vs. Previous Five Winters
Comparing the 2024-2025 winter season’s snowfall to the previous five seasons requires examining the actual snowfall data as the season progresses. However, we can analyze trends from the previous five winters to make some general observations. For example, the winter of 2019-2020 saw above-average snowfall across much of Pennsylvania, while 2021-2022 experienced a relatively mild winter with below-average snowfall in many regions.
These variations highlight the inherent unpredictability of winter weather in Pennsylvania. Any prediction for 2024-2025 would need to consider factors like the El Niño Southern Oscillation (ENSO) pattern and other long-range weather forecasting models, but ultimately, precise snowfall predictions for the entire season are difficult to make with certainty far in advance. Real-time weather monitoring throughout the winter season will be necessary for accurate assessment of snowfall amounts.
Predictive Models and Forecasting Methods
Accurately predicting snowfall in Pennsylvania, especially months in advance, is a complex undertaking that relies on sophisticated weather models and the careful analysis of various meteorological data points. These predictions are not simply educated guesses; they are the result of intricate computations and probabilistic assessments based on historical data and current atmospheric conditions.Predicting snowfall involves integrating various atmospheric variables to create a comprehensive picture of upcoming weather patterns.
This integration relies heavily on numerical weather prediction (NWP) models, which are computer programs that solve complex equations describing the atmosphere’s behavior. These models ingest vast amounts of data, including temperature, pressure, humidity, wind speed and direction, and precipitation type, to simulate the atmosphere’s evolution over time.
Checking the snow predictions for Pennsylvania in 2024-2025, using a detailed map, is a great way to plan winter activities. If significant snowfall is anticipated in January 2025, you might want to check out this helpful resource for ideas on things to do in January 2025 , ensuring you make the most of the snowy season. Remember to always consult updated snow predictions before finalizing your plans for Pennsylvania.
Weather Models Used for Snow Predictions
Several different NWP models are employed for snow predictions, each with its strengths and limitations. The Global Forecast System (GFS), for example, is a global model providing broad-scale predictions, useful for identifying large-scale weather systems that might impact Pennsylvania. However, its resolution is relatively coarse, meaning it may not capture the fine details of local snowfall variations. In contrast, higher-resolution models like the North American Mesoscale (NAM) model provide more localized predictions, offering greater detail on snowfall amounts and location but with a smaller geographical coverage area.
Predicting Pennsylvania’s snowfall for 2024-2025 is a complex task, relying on various meteorological factors. To gauge how far out we are from potential winter storms, it’s helpful to know the timeframe; you can check exactly how many days remain until January 19th, 2025, by visiting this site: how many days till january 19 2025. This date could be a significant marker for snowfall predictions, providing a point of reference for assessing the likelihood of significant accumulation in the coming months.
The European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF) model is also frequently used and is often considered to have higher accuracy in long-range forecasting, though its computational demands are high. The choice of model depends on the desired level of detail and the timeframe of the prediction.
Utilizing Meteorological Data for Snow Predictions
Meteorological data plays a crucial role in generating snow predictions. Temperature profiles, particularly at different altitudes, are essential for determining whether precipitation will fall as snow or rain. The presence of a cold air mass aloft is crucial for snow formation. Atmospheric pressure gradients help predict the movement and intensity of weather systems. High pressure systems generally bring clear skies, while low-pressure systems are often associated with precipitation.
Humidity levels indicate the amount of moisture available for snowfall. The interplay of these factors, combined with sophisticated algorithms within the NWP models, helps forecasters estimate snowfall amounts and timing. For example, a high-pressure system moving in from Canada might bring cold, dry air, resulting in little to no snow, while a low-pressure system tracking in from the Atlantic could bring warm, moist air, resulting in significant snowfall if temperatures are sufficiently cold at the surface.
Challenges in Accurate Snowfall Prediction
Accurately predicting snowfall, especially several months in advance, presents significant challenges. The atmosphere is a chaotic system, meaning small initial uncertainties in data can lead to large differences in predictions over time. This is particularly true for long-range forecasts. The complexity of the interactions between various atmospheric factors, coupled with the limitations of even the most advanced NWP models, contributes to prediction uncertainties.
Furthermore, factors like terrain elevation and proximity to large bodies of water significantly influence snowfall patterns, making accurate prediction in a geographically diverse region like Pennsylvania particularly challenging. For instance, while a model might accurately predict the overall snowfall for the state, the amount in the Pocono Mountains will likely differ significantly from the amount in Philadelphia due to these localized factors.
Finally, even with sophisticated models and ample data, unforeseen events, such as sudden changes in atmospheric patterns, can dramatically affect snowfall predictions, leading to discrepancies between the forecast and reality.
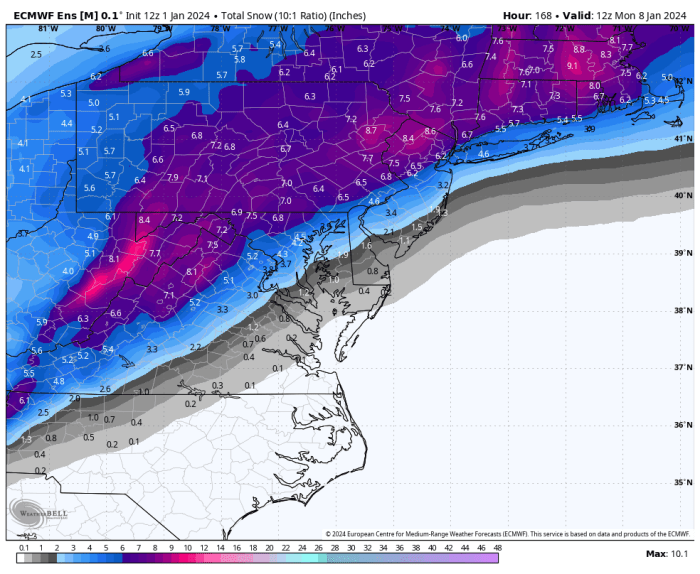
Visualizing Snow Predictions

Effective visualization is crucial for understanding and communicating complex weather predictions. Maps and charts provide a readily accessible way to interpret predicted snowfall amounts and probabilities across Pennsylvania for the 2024-2025 winter season. This allows for easier planning and preparation by individuals, businesses, and emergency services.
By employing color-coded maps and comparative charts, we can translate raw data into easily digestible information, highlighting areas of high and low snowfall risk. This section details the design of such visualizations, focusing on clarity and accuracy in representing predicted snowfall patterns.
Conceptual Snowfall Zone Map for Pennsylvania (2024-2025)
The map would depict Pennsylvania divided into color-coded zones representing different snowfall probability levels. For example, a deep purple could indicate a very high probability of significant snowfall (e.g., above 60 inches), while light blue might signify a low probability of minimal snowfall (e.g., below 10 inches). The Allegheny Mountains would likely be depicted in a darker shade, reflecting their higher elevation and typical higher snowfall.
Planning a trip based on snow predictions for Pennsylvania in 2024-2025? Accurate forecasting is key, especially if you’re considering attending a relevant conference like the american public health association conference 2025 , which might influence your travel plans. Therefore, carefully checking the Pennsylvania snow predictions map will be essential for a smooth journey, regardless of your conference attendance.
Areas near Lake Erie could also show increased probability of snowfall due to lake-effect snow. The transition between zones would be gradual, reflecting the changing probability of snowfall across the state. Cities and major towns would be marked for easy reference. A legend would clearly define each color and its corresponding snowfall probability range.
Predicted Snowfall Accumulation Comparison Chart
The following table provides a sample comparison of predicted snowfall accumulation for different regions of Pennsylvania. Note that these are illustrative examples and actual predictions will vary depending on the specific forecasting model used and the evolving weather patterns.
Planning for Pennsylvania’s potential snowfalls in 2024-2025, using the available snow predictions map, is a good starting point for winter preparedness. However, looking ahead to the summer, securing a position is equally important, and you might consider applying for healthcare consulting internships summer 2025 for valuable experience. Returning to the snow predictions, remember to check the map regularly for updates as winter approaches.
| Region | Predicted Snowfall (inches) | Probability Range |
|---|---|---|
| Northeast Pennsylvania (Pocono Mountains) | 70-90 | High (70-80%) |
| Northwest Pennsylvania (Erie Region) | 50-70 | Medium-High (60-70%) |
| Central Pennsylvania (State College Area) | 30-50 | Medium (40-50%) |
| Southeast Pennsylvania (Philadelphia Area) | 10-20 | Low (20-30%) |
| Southwest Pennsylvania (Pittsburgh Area) | 35-55 | Medium (45-55%) |
Key Elements of a Comprehensive Snow Prediction Map
A comprehensive snow prediction map requires careful consideration of several key geographic and meteorological factors to ensure accuracy and usefulness. The following points highlight these essential elements:
- Elevation: Higher elevations typically receive significantly more snowfall than lower elevations due to orographic effects (lifting of air masses over mountains).
- Proximity to Water Bodies: Lake-effect snow can dramatically increase snowfall in areas downwind of large lakes, such as Lake Erie in Pennsylvania.
- Topography: The shape of the land influences wind patterns and snowfall distribution. Valleys may accumulate more snow due to wind convergence.
- Geographic Features: Mountains, hills, and valleys significantly affect snowfall patterns. These features should be clearly represented on the map.
- Probability Levels: The map should clearly indicate the probability of different snowfall amounts, not just the predicted amount. This allows for better risk assessment.
- Data Sources: The map should clearly cite the data sources used for the prediction, ensuring transparency and accountability.
- Timeframe: The map should specify the timeframe of the prediction (e.g., 24 hours, 7 days, entire winter season).
Impact of Snowfall on Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania’s economy and infrastructure are significantly impacted by snowfall, particularly during periods of heavy accumulation. The effects ripple across various sectors, leading to both immediate disruptions and long-term economic consequences. Understanding these impacts is crucial for effective preparedness and mitigation strategies.Snowfall significantly affects Pennsylvania’s economy across multiple sectors. The state’s diverse economy, encompassing agriculture, tourism, and a robust transportation network, makes it particularly vulnerable to the economic repercussions of severe winter weather.
Economic Consequences of Heavy Snowfall
Heavy snowfall in Pennsylvania disrupts transportation networks, leading to significant economic losses. Closures of highways and airports cause delays in the delivery of goods, impacting businesses reliant on timely supply chains. For example, the blizzard of 2016 caused widespread transportation disruptions, resulting in millions of dollars in losses for businesses across the state. The agricultural sector also suffers, with livestock facing challenges and delays in harvesting and distribution of produce.
The tourism industry, a major contributor to Pennsylvania’s economy, experiences a downturn during severe snowstorms as tourists cancel trips and attractions close. The overall economic impact from lost productivity, damage to infrastructure, and decreased consumer spending can be substantial. The economic costs extend beyond immediate losses, affecting long-term investments and potentially impacting future economic growth.
Risks Associated with Significant Snowfall
Significant snowfall presents various risks to Pennsylvanians. Power outages are a common consequence of heavy snow and ice accumulation on power lines, leading to disruptions in essential services and potential damage to property. Transportation disruptions, including road closures and flight cancellations, isolate communities and hinder access to essential services like healthcare. Property damage from collapsing roofs due to heavy snow accumulation or burst pipes from freezing temperatures adds further economic strain.
Furthermore, the increased risk of accidents due to hazardous road conditions leads to injuries and fatalities, imposing significant costs on individuals and the healthcare system. The potential for cascading failures, where one disruption triggers others (e.g., power outage leading to heating system failure), amplifies the overall risk.
Preparedness Measures for Major Snowfall
Effective preparedness is key to mitigating the negative impacts of major snowfall. Planning ahead and taking proactive measures can significantly reduce risks and minimize disruptions.
Before a major snowfall:
- Stock up on essential supplies, including food, water, medications, and batteries.
- Prepare an emergency kit with a flashlight, first-aid supplies, and blankets.
- Ensure your car is winterized with appropriate tires, fluids, and emergency supplies.
- Develop a communication plan with family and friends in case of power outages or transportation disruptions.
During a major snowfall:
- Limit travel unless absolutely necessary.
- Stay informed about weather updates and emergency alerts.
- Conserve energy to prevent power outages.
- Check on vulnerable neighbors and family members.
After a major snowfall:
- Clear snow and ice from walkways and driveways.
- Check for damage to your property and report any issues to the appropriate authorities.
- Be aware of potential hazards, such as downed power lines.
- Monitor for any further weather alerts and follow instructions from emergency services.
Snowfall and Climate Change in Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania’s snowfall patterns are undergoing shifts, and understanding the relationship between these changes and climate change is crucial for effective planning and adaptation. Analyzing historical snowfall data alongside current trends reveals a complex picture influenced by various climatic factors, many of which are being altered by a warming planet.Climate change is projected to significantly influence the intensity and frequency of snowfall events in Pennsylvania.
While overall average snowfall might decrease in some regions, the intensity of individual storms could increase, leading to more frequent periods of heavy snowfall. This is because warmer temperatures increase atmospheric water vapor capacity, meaning that when snow does fall, there’s more moisture available to create heavier snowfalls. This can result in more severe and disruptive snowstorms, even if the overall annual snowfall is lower.
Conversely, warmer temperatures can also lead to more rain events, reducing the likelihood of snowfall in some areas and at certain times of the year.
Changes in Snowfall Trends and Their Causes, Snow predictions pennsylvania 2024 2025 map
Comparing historical snowfall records, readily available from the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) and Pennsylvania State Climatologist, with recent data reveals a noticeable trend in certain regions. For example, some areas that historically experienced consistent, moderate snowfall may now see less frequent but more intense snow events. Other areas may experience a shift towards more rain-on-snow events, leading to significant icing and hazardous conditions.
These changes are largely attributed to rising average temperatures, which influence the phase of precipitation (snow vs. rain) and alter the atmospheric dynamics that drive winter storms. The increased frequency of extreme weather events, including heavy snowfall and rapid snowmelt, is also a notable consequence of climate change. For instance, the winter of 2015-2016 saw record-breaking snowfall in parts of the state, while other recent winters have experienced significantly less overall accumulation.
These fluctuations highlight the unpredictability introduced by climate change.
Impact on Water Resources
Altered snowfall patterns significantly impact Pennsylvania’s water resources. Snowpack acts as a natural reservoir, slowly releasing meltwater into rivers and streams throughout the spring. Reduced snowfall or accelerated snowmelt due to warmer temperatures can lead to decreased spring runoff, impacting water availability for agriculture, industry, and human consumption, particularly during drier summer months. Conversely, intense snowfall events followed by rapid melting can cause flash flooding and increased erosion.
This variability in water availability poses challenges for water management strategies across the state. For example, municipalities relying on snowmelt for drinking water supplies may need to invest in alternative sources or develop more robust water conservation plans.
Ecosystem Impacts
Changes in snowfall patterns have far-reaching consequences for Pennsylvania’s ecosystems. Snow cover provides insulation for plants and animals, protecting them from extreme cold. Reduced snow cover duration can increase winter mortality among certain species, disrupt plant life cycles, and alter the timing of spring migration and breeding. Furthermore, changes in snowmelt timing can affect the availability of water for aquatic ecosystems, impacting fish populations and other aquatic life.
For instance, early snowmelt can lead to lower water levels in streams during critical periods for fish spawning and juvenile development. The increased frequency of extreme weather events also presents challenges to the resilience of various ecosystems.